
Das Projekt FUSION ist ein auf fünf Jahre angelegtes Großvorhaben der Universität Siegen und wird im Rahmen des Programms „Innovative Hochschule“ vom Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) gefördert.
Zielsetzung des Projektes ist es, die Weiterentwicklung der Universität mit Herausforderungen der Regionalentwicklung in Südwestfalen und angrenzenden Kommunen zu verbinden. Auf Seiten der Universität geht es darum, neue Formen der Zusammenarbeit zwischen Wissenschaftsdisziplinen und Fakultäten zu entwickeln, die das Forschungsprofil erweitern und innovative Lehrangebote ermöglichen.
Der Lehrstuhl für Werkstoffsysteme für den Fahrzeugleichtbau leitet das Teilvorhaben 3 „Ressourcenschonung & Dekarbonisierung“.

Das ZIM-Projekt „Entwicklung eines innovativen Fahrzeugrückhaltesystems mit hybriden Crashabsorbern und einer integrierten Crashsensorik zur Absicherung von Einmündungen und örtlichen Gefahrstellen“ zielte darauf ab, ein innovatives Fahrzeugrückhaltesystem mit hybriden Crashabsorbern und integrierter Crashsensorik zu entwickeln, um Einmündungen und örtliche Gefahrenstellen sicherer zu machen. Dies wurde durch die Entwicklung eines anpassungsfähigen und effektiven Crashabsorbers ermöglicht.
Das Projekt wurde zusammen mit den Partnern PASS+CO, sowie dem Lehrstuhl Automotive Lightweight Design (LiA) der Universität Paderborn durchgeführt.
Cyclic Strength of an Intrinsic Hybrid Material

- Mechanical characterization of the materials interface between glass fiber reinforced plastic (GFRP) and high strength steel for a cyclically loaded component
- Mechanical and fatigue testing of the hybrid laminate under conditions of tensile, bending, and shear loads, respectively
- X-ray analysis of residual stress in the metallic part
- Numerical calculation of residual stress in GFRP
- Mechanical characterization of the fatigue strength with consideration of residual stress
- Load-adapted lightweight design of the hybrid component
Brandt, R. et al.: InHyb – An Intrinsic Hybrid Laminate for Cyclically Loaded Components. Proceedings der 4. Internationalen Konferenz Hybrid. 2020
Short Crack Propagation in a Martensitic Spring Steel

- Estimation of the residual stress impact on the fatigue strength of martensitic springs steel
- In situ investigation of the short crack propagation by means of miniature testing machines
- Microstructural analysis of short crack propagation by means of electron back scattering diffraction (EBSD)
- Material-scientific, numerical modelling of the short crack growth behavior by means of a boundary element method
Short Crack Propagation in a Martensitic Spring Steel

- Alloy development of a high strength, stainless spring steel by substitution of nickel with manganese
- X-ray phase and texture analyses for a quantitative assessment of the precipitation hardening contribution to the overall strength
- Mechanical and electrochemical characterization of the steel grade
- Manufacturing and testing of components
Brandt, R. et al.: The Application of a Stainless Martensitic Precipitation Hardening Steel to an Elastic Spring. Compendium of Modern Spring Technologies. 2021
High Strength Spring Steels with Reduced Low Temperature Creep

- Investigation of the LTC controlling mechanisms in a martensitic spring steel (MSS) by application of a mechanism-based LTC model
- Review and rework of two existing theories (SHT and ECM) based on “dislocation glide” mechanism
- Mechanical testing of the stress s and temperature T dependent LTC behavior of MSS – Validation of the reworked ECM
- Microstructural characterization and quantitative phase analysis of LTC by means of electron back scattering diffraction (EBSD) and X-ray diffraction
Graded High Strength Spring-Steels by a special Inductive Heat Treatment
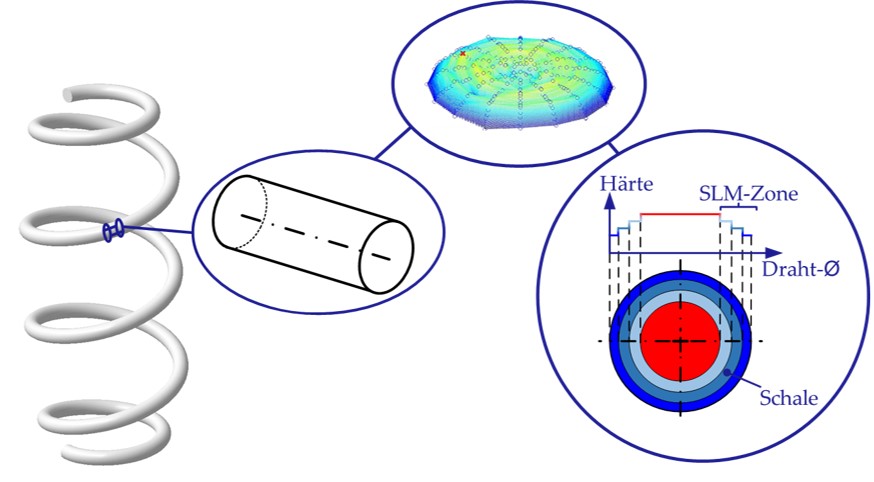
- Surface Layer Modification (SLM) Technology development of an inductive Q&T-process for steel, which creates a hardness gradient from the surface to the core of the material
- Specific sample preparation for mechanical testing from Q&T wires
- Materials characterization and fracture mechanical testing
- Fatigue testing and fracture analysis of fatigued SLM specimens
- 8% of mass reduction compared to springs by means of conventional inductive Q&T technology
Tump, A. et al.: Graded High-Strength Spring-Steels by a Special Inductive Heat Treatment, 2016, doi:10.1088/1757-899X/118/1/012021
The Tooth Root Load-Bearing Capacity of Splines on Hollow Shafts

- Investigation of the influence of the relevant material-related parameters on the static and cyclic strength
- Sample preparation in terms of frequency-modulated axial gear pressing and various variants of Q&T of splines on hollow shafts
- Construction of a testing machine for torsional fatigue testing of hollow shafts
- Materials characterization and mechanical testing of static and fatigue strength
- Stress analysis modelling by means of finite element method
- Quantification of core and surface layer hardness, residual stress, and grain size on the static and cyclic strength
Springorum, J, Werkstoffmechanische Einflussfaktoren auf die Zahnfußtragfähigkeit von Passverzahnungen auf Hohlwellen, 2020

